Etymology[edit]
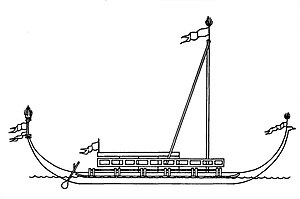
Superstructure of a Visayan caracoa (side view).
Karakoa was usually spelled as "caracoa" during the Spanish period. The name and variants thereof (including caracora, caracore, caracole, corcoa, cora-cora, and caracolle) were used interchangeably with various other similar warships from maritime Southeast Asia, like the kora kora of the Maluku Islands.[1][2]
The origin of the names are unknown. Some authors propose that it may have been derived from Arabic qurqur (pl. qaraqir) meaning "large merchant ship" via Portuguese caracca (carrack). However, this is unlikely as the oldest Portuguese and Spanish sources never refer to it as "caracca", but rather "coracora", "caracora" or "carcoa". The Spanish historian Antonio de Morga explicitly says that the name karakoa is ancient and indigenous to the Tagalog people in Sucesos de las Islas Filipinas (1609). There are also multiple cognates in the names of other vessels of Austronesian vessels (some with no contact with Arab traders) like the Ivatan karakuhan, Malay kolek, Acehnese kolay, Maluku kora kora, Banda kolekole, Motu kora, and the Marshallese korkor. Thus it is more likely that it is a true Malayo-Polynesian word and not a loanword.[3]
Description[edit]
Karakoa were similar to and were sometimes confused with balangay, but can be differentiated in that they possessed raised decks (burulan) amidships and on the outriggers, as well as S-shaped outrigger spars. They also had sharply curved prows and sterns, giving the ships a characteristic crescent shape. Their design was also sleeker and faster than balangay, even though karakoa were usually much larger. Like balangay, they can be used for both trade and war. Their main use, however, were as warships and troop transports during the traditional seasonal sea raids (mangayaw) or piracy (especially against European trade ships). They were estimated to have speeds of up to 12 to 15 knots.[4][5][6][7][8]
The Spanish priest Francisco Combés described karakoa in great detail in 1667. He was also impressed by the speed and craftsmanship of the vessels, remarking:[10]
"That care and attention, which govern their boat-building, cause their ships to sail like birds, while ours are like lead in this regard."
—
Francisco Combés, Historia de las islas de Mindanao, Iolo y sus adyacentes (1667)
Like other outrigger vessels, karakoa had very shallow drafts, allowing them to navigate right up to the shoreline. The hull was long and narrow and was made from lightweight materials. The entire vessel can be dragged ashore when not in use or to protect it from storms.[5][7][8]
The keel was essentially a dugout made from the single trunk of hardwoods like tugas (Vitex parviflora) or tindalo (Afzelia rhomboidea). Strakes were built up along the sides of the keel, forming the hull. They were usually made from lawaan wood (Shorea spp.) and were tightly fitted to the keel and with each other by dowels reinforced further with fiber lashings (usually from sugar palm) on carved lugs. Ribs for support and seating connected the strakes across, which were also lashed together with fiber. The use of dowels and lashings instead of nails made the hull flexible, able to absorb collisions with underwater objects that would have shattered more rigid hulls. Strongly curved planks were fitted at both ends of the keel, giving the ship a crescent-shaped profile. These were usually elaborately carved into serpent or dragon (naga) designs. Tall poles festooned with colorful feathers or banners were also affixed here, called the sombol (prow) and the tongol (stern).[note 1] The anterioposterior symmetry allowed the boat to reverse direction quickly by simply having the rowers turn around in their seats.[5][7][8]
Karakoa had tripod bamboo masts (two or three in larger vessels), rigged with either crab-claw sails or rectangular tanja sails (lutaw). The sails were traditionally made from woven plant fibers (like nipa), but were later replaced with materials like linen. In addition to the sails, karakoa had a crew of rowers (usually from the alipin caste) with paddles (bugsay),[note 2] or oars (gaod or gaor)[note 3] on either side of the hull. In between the rowers was an open space used as a passage for moving fore and aft of the ship. Various chants and songs kept the pace and rhythm of the rowers. Above the rowers was a distinctive raised platform (burulan) made of bamboo where warriors (timawa) and other passengers stood, so as to avoid interfering with the rowers. This platform can be covered by an awning of woven palm leaves (kayang, Spanish: cayanes) during hot days or when it rains, protecting the crew and cargo. Karakoa lacked a central rudder and was instead steered by large oars controlled by the nakhoda (helmsman) seated in a covered structure near the back of the ship. These oars could be raised at a moment's notice to avoid obstructions like shallow reefs.[7][8]
The hull was connected to the outrigger structure, which was composed of the S-shaped crosswise outrigger spars (tadik) attached to the outrigger floats (katig or kate) at water level. The katig provided stability and additional buoyancy, preventing the boat from capsizing even when the hull is entirely flooded with water. The katig, like the hull itself, curve upwards at both ends, minimizing drag and preventing rolling. Katig were usually made with large bamboo poles traditionally fire hardened and bent with heat. In between the katig and the hull was another lengthwise beam called the batangan. This served as the support structure for two additional burulan on either side of the boat called the pagguray, as well as additional seating for rowers called daramba.[7][8]
Karakoa can reach up to 25 metres (82 ft) in length. Very large karakoa can seat up to a hundred rowers on each side and dozens warriors on the burulan.[5][7][8] Vessels of this size were usually royal flagships and were (inaccurately) referred to by the Spanish as joangas or juangas (sing. joanga, Spanish for "junk", native dyong or adyong).[8][12]

 ?ezimgfmt=ng:webp/ngcb45 300w,
?ezimgfmt=ng:webp/ngcb45 300w,  ?ezimgfmt=ng:webp/ngcb45 60w" data-ezsrc="https://filipiknow.net/ezoimgfmt/www.filipiknow.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/Karakoa.jpg?ezimgfmt=rs:550x372/rscb45/ng:webp/ngcb45" />
?ezimgfmt=ng:webp/ngcb45 60w" data-ezsrc="https://filipiknow.net/ezoimgfmt/www.filipiknow.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/Karakoa.jpg?ezimgfmt=rs:550x372/rscb45/ng:webp/ngcb45" />


